NURS307 Physical Exam Competency-1 Documentation Submission
NURS307 Physical Exam Competency-1 Documentation Submission
Here is an example of documentation for your competencies. Include all parts on one word document for that week. This only includes general and thorax as an example. You would also include the cardiac component. This is a narrative documentation. I am looking for your to paint a picture of your assessment in a concise and thorough manner. Be sure to utilize the correct terminology. Remember that in documentation you do not need full sentences, so do not write….patient is alert and oriented……
You are required to demonstrate competency in the physical assessment techniques. You also are required to accurately document your physical assessment findings. These two requirements are worth 70% of your grade. You will find the specific guidelines for these two requirements on the course blackboard. You will be required to video record yourself performing the various assessments and submitting them on blackboard.
ORDER NURS307 Physical Exam Competency-1 Documentation Submission
NURS 307 Abdomen/Nutrition Assessment Flashcards
|
Identify the 2 types of viscera in the abdomen. Which of these percuss tympany? |
Solid viscera |
|
|
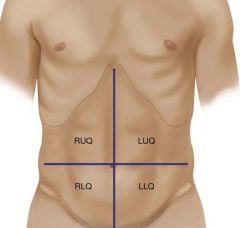
Identify the quadrants in the abdomen. |
RUQ |
|
|
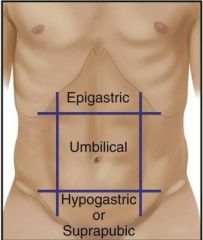
Identify and describe the 3 regions of the abdomen. |
Epigastric – above belly button Umbilicus – around belly button area Hypogastric/Suprapubic – below belly button, above pubic region |
|
|
Identify the nationalities that have increased risk for lactose intolerance at birth. |
African Americans, Native Americans, Asians, and Mediterranean groups |
|
|
abdomen |
large oval cavity extending from diaphragm down to the brim of the pelvis |
|
|
Identify what organs/structures are in the RUQ. |
liver, gallbladder, duodenum, head of pancreas, R kidney and adrenal, hepatic, flexure of colon, part of ascending and transverse colon |
|
|
Identify what organs/structures are in the LUQ |
stomach, spleen, L lobe of liver, body of pancreas, L kidney and adrenal, splenic flexure of colon, part of transverse and descending colon |
|
|
Identify what organs/structures are in the LLQ. |
part of descending colon, sigmoid, colon, L ovary and tube, L ureter, L spermatic cord |
|
|
Identify what organs/structures are in the RLQ. |
cecum, appendix, R ovary and tube, R ureter, R spermatic cord |
|
|
Identify the common chief complaint for abdomen. |
Abdominal pain, unspecific |
-
CONT
|
Identify the normal range in frequency for bowel movements. |
o Frequent 2-3 times per day |
|
|
Should feces be floating or sinking? |
It should be sinking. If it’s floating, it means patient is not getting enough fiber. |
|
|
If a patient is vomiting/having diarrhea more than ______ times a day, you will be concerned about dehydration. |
five |
|
|
Why must you auscultate before palpation and percussion? |
If you percuss or palpate first, you will create gurgles/sounds in the abdomen. |
|
|
Identify the 4 descriptions of bowel sounds. |
Normal (normoactive) |
|
|
What does it mean when you hear a bruit when checking for vascular sounds? |
It could mean there is an aneurysm. |
|
|
Identify the 2 types of sound you would hear via percussion. |
Tympany and dullness |
|
|
pyelonephritis |
Inflammation of the kidney and its pelvis, caused by bacterial infection. |
|
|
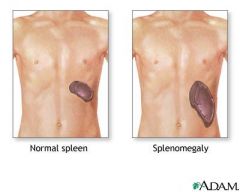
organomegaly |
abnormal enlargement of organs Pic: Spleen enlargement |
|
|
Describe the two types of palpation. |
Light – 1 cm Deep – 2-3 inches |
-
CONT
|
ascites
|
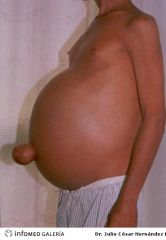 accumulation of serous fluid in the peritoneal cavity
|
|
|
constipation
|
bowels are evacuated at long intervals or with difficulty/straining,
stool is usually very hard
|
|
|
umbilical hernia
|
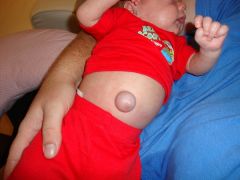 soft skin covered mass which is the protrusion of the intestine
through a weakness or incomplete closure in the umbilical ring
Note: When person is relaxed, you should be able to retract this into belly. |
|
|
hepatitis
|
inflammation and usually enlarged liver
|
|
|
gastroesophageal reflux (GER/GERD)
|
complex of symptoms of
esophagitis, heartburn, usually occurs 30-60 minutes after eating, aggravated by lying down or bending over, (in infants characterized by spitting up/vomiting)
|
|
|
aortic aneurysm
|
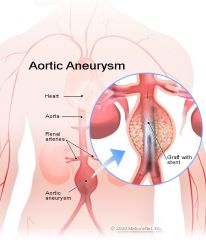 pulsating mass in the upper abdomen just left of midline; positive bruit, decreased femoral pulses
Note: 80% are palpable during routine physical exam |
|
|
Describe pain related to appendicitis.
|
diffuse pain in periumbilical region that later shifts to severe, sharp, persistent pain and tenderness localized in RLQ (McBurney’s point)
|
|
|
Appendicitis pain is aggravated by _________. (2)
It is associated with the following symptoms: __________. (3) |
aggravated by movement, coughing
anorexia, N/V, fever |
|
|
gastroenteritis/gastritis (AGE)
|
diffused generalized abdominal pain with nausea and diarrhea
|
|
|
cholecystitis
|
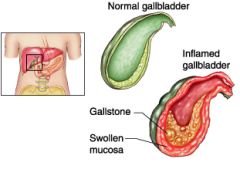 inflammation of the gallbladder
|
|
Describe the clinical manifestation of cholecystitis and its causes.
|
Sudden pain in RUQ that may radiate to right or left scapula and which builds over time, lasting 2-4 hours after ingestion of fatty foods, alcohol, or caffeine
|
|
|
Cholecystitis is common in ______.
|
females > 40 years old.
|
|
|
A bruit indicates _________ in _________ vessels.
|
turbulent blood flow
in constricted, abnormally dilated, or tortuous vessels |
|
|
What result confirms rebound tenderness (Blumberg sign)?
|
Pain on release of pressure
|
|
|
Describe how to perform the following test: rebound tenderness. What is normal response?
|
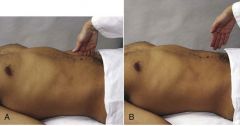 Choose a site away from the painful area. Hold your hand 90 degrees, or perpendicular, to the abdomen. Push down slowly and deeply; then lift up quickly.
A normal, or negative, response is no pain on release of pressure. |
|
|
Describe how to perform the following test: inspiratory arrest (Murphy Sign). What is a normal response?
|
Hold your fingers under the liver border. Ask the person to take a deep breath.
A normal response is to complete the deep breath without pain. |
|
|
Describe how to perform the following test: iliopsoas muscle test.
|
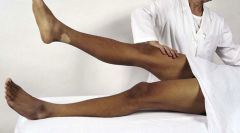 With the person supine, lift the right leg straight up, flexing at the hip (Fig. 21-31); then push down over the lower part of the right thigh as the person tries to hold the leg up.
|
|
|
Identify the 5 locations you would listen for vascular sounds.
|
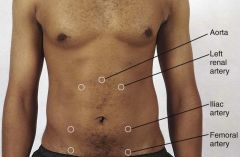 Aorta
L/R renal artery L/R iliac artery L/R femoral artery |
|
|
hepatomegaly
|
enlarged liver
|
|
|
Hypoactive or absent bowel sounds typically follow ___________. (2)
|
abdominal surgery or inflammation of the peritoneum
|
|
peritoneum
|
serous membrane lining the cavity of the abdomen and covering the abdominal organs
|
|
|
An individual is 5′ 3” in height and weighs 120 pounds. What is their BMI?
|
 21.3
|
|
|
apple shape vs. pear shape
|
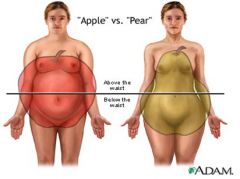 Apple – Wider waist than hips
Pear – Wider hips than waist |
|
|
Which of the following has a higher risk for heart disease: apple shape or pear shape?
|
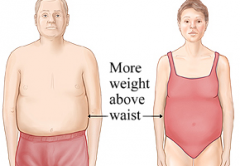 Apple shape
|
|
|
Describe how to calculate waist/hip ratio.
|
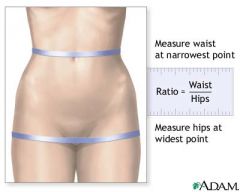 Ratio = Waist/Hips
|
|
|
Identify the formula for BMI using inches and pounds.
|
 |
|
|
Perform the iliopsoas muscle test when ________ is suspected.
|
appendicitis
|
|
|
What is the normal result for iliopsoas muscle test?
|
No pain/change
|
|
|
When the iliopsoas muscle is inflamed (which occurs with an inflamed or perforated appendix), pain is felt the ______ quadrant.
|
RLQ
|
|
|
TRUE/FALSE
Evidence shows that the Obturator Test, another technique that stretches the obturator muscle, does not work to diagnose appendicitis. |
True
|
|
Sharp pain during CVA tenderness test indicates __________.
|
Sharp pain occurs with inflammation of the kidney or paranephric area.
|
|
|
Describe how to perform the following test: CVA tenderness. What is normal response?
|
To assess the kidney, place one hand over the twelfth rib at the costovertebral angle on the back (Fig. 21-17). Thump that hand with the ulnar edge of your other fist.
Normal response is no pain. |
|
|
Identify the disease/condition the following patient may have.
You feel a pulsating mass in the upper abdomen. You hear a bruit in that region and the pt has decreased femoral pulses. |
Aortic aneurysm
|
|
|
Identify the disease/condition the following patient may have.
Pt has had increasing pain in the RLQ. The pain started in the preumbilical region and has gotten worse and moved to the RLQ. |
Appendicitis
|
|
|
Identify the disease/condition the following patient may have.
Pt has abdominal pain throughout belly. He/She is also experiencing nausea and diarrhea. |
Gastroenteritis/gastritis
|
|
|
Identify the disease/condition the following patient may have.
Pt reports pain lasting ~3 hours after ingesting fatty foods and caffeine. The pain is in the RUQ. |
Cholecystitis
|
|
|
Identify the disease/condition the following patient may have.
Pt feels heartburn ~30 minutes after eating. He said it feels worst after lying down or bending over. |
gastroesophageal reflux (GER/GERD)
|
|
|
Blumberg sign = _______ test
|
rebound tenderness
|
|
|
Murphy sign = _______ test
|
inspiratory arrest
|